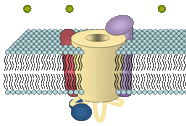
Dayal A., Schrötter K., Pan Y., Föhr K., Melzer W. & Grabner M. (2017) The Ca2+ influx trough the mammalian skeletal muscle dihydropyridine receptor is irrelevant for muscle performance. Nature Communications 8.475 DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00629-x
Schrötter K.*, Dayal A.* & Grabner M. (*both authors contributed equally to this work) (2017) The mammalian skeletal muscle DHPR has larger Ca2+ conductance and is phylogenetically ancient to the early ray-finned fish sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus). Cell Calcium. 61: 22-31
Dayal A., Bhat V., Franzini-Armstrong, C. & Grabner M. (2013) Domain-cooperativity in the β1a subunit is essential for dihydropyridine receptor voltage sensing in skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 110(18): 7488-93
Pirone A., Schredelseker J., Tuluc P., Gravino E., Fortunato G., Flucher B.E., Carsana A., Salvatore F. & Grabner M. (2010) Identification and functional characterization of malignant hyperthermia mutation T1354S in the outer pore of the Cavα1S-subunit. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299(6):C1345-54
Dayal A., Schredelseker J., Franzini-Armstrong C. & Grabner M. (2010) Skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling is independent of a conserved heptad repeat motif in the C-terminus of the DHPR β1a subunit Cell Calcium 47(6):500-6
Schredelseker J., Shrivastav M., Dayal A. & Grabner M. (2010) Non-Ca2+-conducting Ca2+ channels in fish skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 107(12): 5658-63
Schredelseker J.*, Dayal A.*, Schwerte T., Franzini-Armstrong C. & Grabner M. (*both authors contributed equally to this work) (2009). Proper restoration of excitation-contraction coupling in the dihydropyridine receptor β1-null zebrafish relaxed is an exclusive function of the β1a subunit. J. Biol Chem. 284(2): 1242-1251
Schredelseker J., Di Biase V., Obermair G.J., Felder E.T., Flucher B.E., Franzini-Armstrong C. & Grabner M. (2005). The β1a subunit is essential for the assembly of dihydropyridine-receptor arrays in skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 102(47): 17219-24
Obermair G.J., Kugler G., Baumgartner S., Tuluc P., Grabner M. & Flucher B.E. (2005). The Ca2+ channel α2δ-1 subunit determines Ca2+ current kinetics in skeletal muscle but not targeting of α1S or excitation-contraction coupling. J Biol. Chem. 280: 2229-2237
Takekura H., Paolini C., Franzini-Armstrong C., Kugler G., Grabner M. & Flucher B.E. (2004). Differential contribution of skeletal and cardiac II-III loop sequences to the assembly of dihydropyridine-receptor arrays in skeletal muscle. Mol. Biol. Cell 15: 5408-5419
Weiss R.G., O'Connell K.M., Flucher B.E., Allen P.D., Grabner M. & Dirksen R.T. (2004). Functional analysis of the R1086H malignant hyperthermia mutation in the DHPR reveals an unexpected influence of the III-IV loop on skeletal muscle EC coupling. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 287(4): C1094-1102
Kugler G., Weiss R.G., Flucher B.E. & Grabner M. (2004). Structural requirements of the dihydropyridine receptor α1S II-III loop for skeletal-type excitation-contraction coupling. J Biol Chem. 279(6): 4721-4728
Flucher B.E., Weiss R.G. & Grabner M. (2002). Cooperation of two-domain Ca2+ channel fragments in triad targeting and restoration of excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 99(15): 10167-10172
Wilkens C.M., Kasielke N., Flucher B.E., Beam K.G. & Grabner M. (2001). Excitation-contraction coupling is unaffected by drastic alteration of the sequence surrounding residues L720-L764 of the α1S II-III loop. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 98(10): 5892-5897
Flucher B.E., Kasielke N. & Grabner M. (2000). The triad targeting signal of the skeletal muscle calcium channel is localized in the COOH terminus of the &alpha1S subunit. J Cell Biol. 151(2): 467-78
Grabner M., Dirksen R.T., Suda N. & Beam K.G. (1999). The II-III loop of the skeletal muscle dihydropyridine receptor is responsible for the Bi-directional coupling with the ryanodine receptor. J Biol Chem. 274(31): 21913-21919
Grabner M., Dirksen R.T. & Beam K.G. (1998). Tagging with green fluorescent protein reveals a distinct subcellular distribution of L-type and non-L-type Ca2+ channels expressed in dysgenic myotubes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 95(4): 1903-8